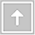
1. Võng mạc là gì?
Võng mạc là một lớp ở tận trong cùng của mắt nó hoạt động giống như lớp film ở máy ảnh.
Sóng ánh sáng tác động tới mắt rồi hội tụ ở trên võng mạc kích thích lớp sợi thận kinh hoạt động rồi gửi thông tin tới não sẽ quyết định chúng ta nhìn thấy gì.
2. Bong võng mạc là gì?
Bong võng mạc có điều kiện là võng mạc tách lớp mô đệm do đó võng mạc mất chức năng.
Có 3 dạng bong võng mạc:
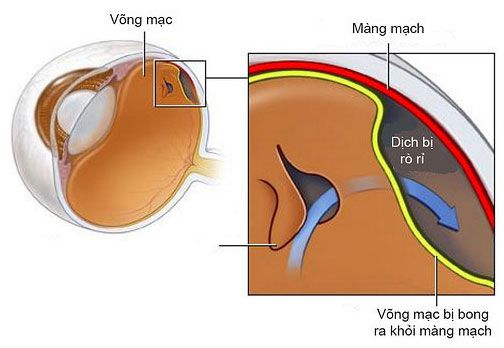
2.1 Bong võng mạc có lỗ rách
Xảy ra thứ phát do sự xâm nhập của dịch xuống dưới lớp võng mạc. Võng mạc tách rời so với lớp đệm.
2.2 Bong võng mạc thể tiết dịch
Xảy ra thứ phát do viêm hoặc do vết thương tụ dịch dưới lớp đệm
2.3 Bong võng mạc co kéo
Xảy ra khi sẹo co kéo võng mạc ra khỏi lớp mô bên dưới
3. Nguyên nhân của bong võng mạc có lỗ rách
Xảy ra với tỷ lệ 1/10000 dân số và ở độ tuổi trung niên. Phổ biến hơn với những người bị cận thị và nguy cơ cao hơn với người có độ cận thị cao hơn.
Bong võng mạc cũng có thể xảy ra sau phẫu thuật mắt, phổ biến nhất là với tỷ lệ 0,3%
Chấn thương là một nguyên nhân khác dẫn đến bong võng mạc.
4. Triệu chứng của bong võng mạc
Bong võng mạc thường bắt đầu bằng sự bóc tách thủy tinh thể phía sau( PVD). Các triệu chứng liên quan đến bóc thủy tinh thể ở phía sau gồm khởi phát đột ngột và chớp sáng. Tuy nhiên, trong một nhóm nhỏ, tách thủy tinh thể ở phía sau có thể gây ra rách võng mạc, có thể tiến triển thành bong võng mạc.
5. Chẩn đoán bong võng mạc
Một bác sỹ nhãn khoa có thể chẩn đoán được thông qua soi đáy mắt khi đồng tử giãn
6. Điều trị có thực sự cần thiết?
Bong vọng mạc có lỗ rách là một cấp cứu nhãn khoa và phẫu thuật là cần thiết để ngăn ngừa mất thị lực vĩnh viễn.
Mục đích của điều trị là đóng võng mạc bằng laser hoặc liệu pháp áp lạnh (phương pháp đông lạnh), loại bỏ dịch dưới võng mạc để làm phẳng nó và hỗ trợ võng mạc.
7. Quan điểm điều trị bong võng mạc
7.1 Laser có thể được sử dụng để điều trị bong võng mạc và ngăn ngừa sự tiến triển của bong võng mạc. Điều này thường được chọn nếu bong võng mạc nhỏ và cục bộ, và nếu hoàng điểm không liên quan.
7.2 Bơm hơi và tạo bóng khí là một kỹ thuật trong đó một bong bóng khí được bơm vào mắt. Bong bóng là một lực chống lại võng mạc tách ra, đẩy nó phẳng vào thành trong của mắt. Điều này thích hợp trong các trường hợp được lựa chọn.
7.3 Phẫu thuật đai độn củng mạc là phẫu thuật sử dụng đai/độn silicon ép củng mạc từ phía ngoài giúp võng mạc ép vào củng mạc được dễ dàng. PT này thường kèm theo bơm khí nội nhãn để kết hợp ép võng mạc từ phía trong và lạnh đông củng mạc.