MENUMENU
- Home
- About us
- About usBệnh viện mắt quốc tế – DND là bệnh viện chuyên khoa mắt công nghệ cao với đội ngũ bác sĩ dày dặn kinh nghiệm
- Our historyĐược thành lập từ năm 2011, bệnh viện đã từng bước chuyển mình trong đầu tư công nghệ và nhân lực
- Our vision and missionMục tiêu “Vì đôi mắt cộng đồng” đem lại cho người bệnh dịch vụ và công nghệ hiện đại nhất phù hợp với thu nhập
- Our staff
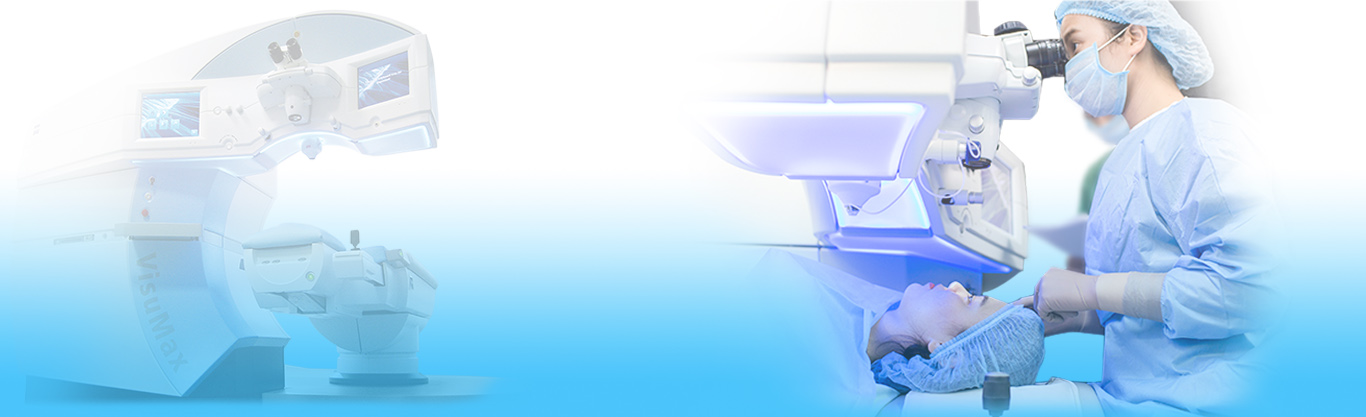
- Our Equipment
- Our divisions
- Recruitment
- Services
- Department of Laser Vision CorrectionTrung tâm khúc xạ. Điều trị và phẫu thuật khúc xạ và lão thị.
- Department of Cataract TreatmentsTrung tâm phẫu thuật Phaco Phẫu thuật điều trị bệnh Đục thủy tinh thể
- Department of Fundus IssuesTrung tâm tầm soát Võng mạc. Điều trị và tầm soát các bệnh lý đáy mắt.
- Department of Diagnostic and TreatmentKhám và điều trị ngoại trú các bệnh lý về mắt.
- Department of Eye Cosmetic SurgeriesTrung tâm điều trị thẩm mỹ vùng mắt và phẫu thuật trung phẫu thẩm mỹ
- Membership CardCác gói thẻ theo dõi và điều trị (Khúc xạ, Đáy mắt), và hỗ trợ ( thẻ Family, thẻ VIP )
- For customers
- News and Events
- Contact us